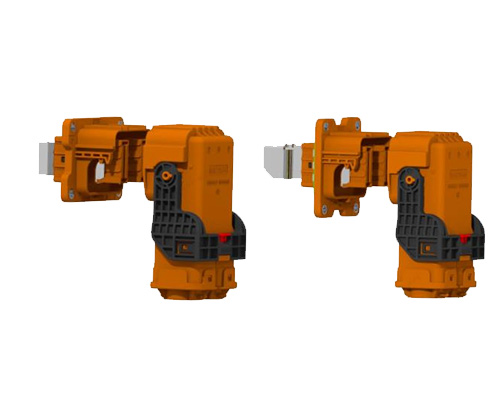
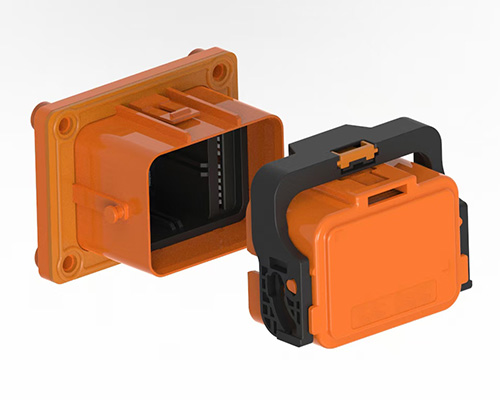
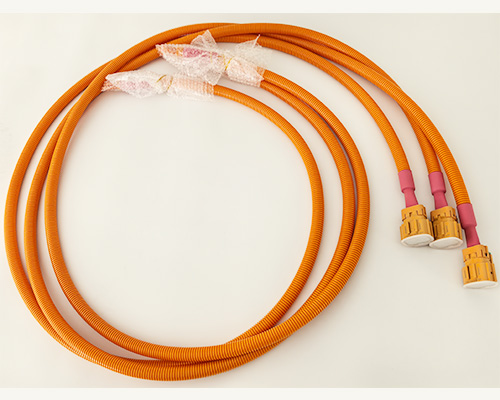
Mode 1, Mode 2, Mode 3, Mode 4 EV Charging Modes
With the growing popularity of electric vehicles, drivers are looking for more than just a charge station. They want a way to get in and out quickly, while still providing a clean experience. The EV charger market is evolving and has become more sophisticated as technology has evolved.
EV Charging can happen in four ways:
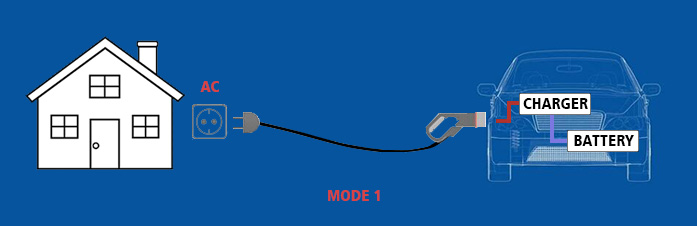
Mode 1 is the slowest mode of home charging, and it uses an alternating current (AC) source. This type of charging takes the longest amount of time (about 40-60 hours) to fully charge the battery. The typical maximum power output of a mode 1 charger is 2.0 kW. If you need to charge faster than that, you're going to need some other options. When using this mode, the vehicle has its own onboard charger (OBC), which converts AC power from the grid into DC power for charging the battery pack.
Mode 1 EV charging is not recommended as it does not require any special protection measures and may cause damage to your vehicle if there are any problems with the extension cord or adapter. The safety concern here is that there may be potential fire hazards due to overvoltage and overload.
For safety reasons, it is necessary to install a dedicated circuit breaker for charging.

Mode 2 charging cable has a 3-pin standard plug at one end, a type 1 or type 2 EV connector at the other end, and an in-line EVSE controller with built-in current limitation in the middle. This allows for remote start/stop, access to current (amps) draw and time remaining until fully charged for safety reasons. The control box also provides functionality like temperature sensing, overcurrent protection and power monitoring.
Benefits of EV charging mode 2: A normal household outlet will allow you to charge your vehicle at home using a mode 2 EV charger made by the car manufacturer or a third-party company. This type of charger does not require any special installation because it plugs directly into an outlet - usually 240 volts at 10amps.

Features:
Mode 3 charging allows for the fast charging of electric vehicles (EVs) to be done at home, work or public locations known as charging stations. This type of charging involves an electric vehicle owner plugging into a dedicated charging station or a home-mounted wall box in order to fast charge their vehicle.
Cable Types:
◆ 1PH 16A 3.6KW Type 2 Charging Cable. Both ends of the cable are with type 2 AC connector.
◆ 1PH 32A 7.2KW Type 2 EV Home Charger. It provides a maximum power level of 7.2 kilowatts single phase 32 amps, with an operation voltage up to 250V.
◆ 3PH 16A 11KW Type 2 Charging Cable. It is performed using a dedicated charging station and/or home mounted wall box.
◆ 3PH 32A 22KW Type 2 AC Fast Charger. It allows the vehicle to be charged much faster than traditional slow charging methods.
◆ Type 1 to Type 2 EV Charging Cable. The cable has two connectors, one is type1 and the other is type2

Mode 4 DC fast charging is a more powerful version of EV charging that can deliver much higher rates of electricity to your vehicle in a short amount of time. This type of charging uses a direct current (DC) connection that delivers energy directly to the vehicle battery.
The charging capacity of Mode 4 charger can up to 350kw. This means that with an consumption of 17 kWh per 100km, you can achieve a recharge for a distance of 100km in just 45 minutes!
Charging Cable:
The charging cables have to be attached permanently to the Fast Charging Station and there is no flexibility in terms of charging positions. The other end of the cable is connected to the CCS2 EV inlet to directly charge the battery.
Mode 4 VS Mode 3:
The difference between mode 4 and mode 3 is that the charging gun of Mode 4 is connected to the AC grid or the DC power supply equipment at the DC grid end, that is, the DC charging pile, which is generally not for household use, but is specially installed at the fast charging station.
The charging current of mode 4 is larger, generally DC 80/125/200/250A, so the charging speed is also the fastest.
EV Charging can happen in four ways:

1. AC Home Slow Charging Mode 1
AC home charging is the most common type of charging and can be done at home. This is where you plug your car into a standard household socket with simple extension cord without any safety measures.Mode 1 is the slowest mode of home charging, and it uses an alternating current (AC) source. This type of charging takes the longest amount of time (about 40-60 hours) to fully charge the battery. The typical maximum power output of a mode 1 charger is 2.0 kW. If you need to charge faster than that, you're going to need some other options. When using this mode, the vehicle has its own onboard charger (OBC), which converts AC power from the grid into DC power for charging the battery pack.
Mode 1 EV charging is not recommended as it does not require any special protection measures and may cause damage to your vehicle if there are any problems with the extension cord or adapter. The safety concern here is that there may be potential fire hazards due to overvoltage and overload.
For safety reasons, it is necessary to install a dedicated circuit breaker for charging.

2. AC Charging Mode 2
Mode 2 charging is useful for emergency situations. Mode 2 is a slow, overnight-style charge where you leave your vehicle plugged in after it has reached full charge to help keep it topped off.Mode 2 charging cable has a 3-pin standard plug at one end, a type 1 or type 2 EV connector at the other end, and an in-line EVSE controller with built-in current limitation in the middle. This allows for remote start/stop, access to current (amps) draw and time remaining until fully charged for safety reasons. The control box also provides functionality like temperature sensing, overcurrent protection and power monitoring.
Benefits of EV charging mode 2: A normal household outlet will allow you to charge your vehicle at home using a mode 2 EV charger made by the car manufacturer or a third-party company. This type of charger does not require any special installation because it plugs directly into an outlet - usually 240 volts at 10amps.

3. AC Fast Charging Technology Mode 3
The most common and standard way to charge electric vehicles is through the mode 3 AC outlet. This is typically the most economical way to charge an electric car or plug-in hybrid vehicle. All public charging stations support this method, so it’s easy to find compatible outlets and adapters at gas stations and shopping plazas on long journeys.Features:
Mode 3 charging allows for the fast charging of electric vehicles (EVs) to be done at home, work or public locations known as charging stations. This type of charging involves an electric vehicle owner plugging into a dedicated charging station or a home-mounted wall box in order to fast charge their vehicle.
Cable Types:
◆ 1PH 16A 3.6KW Type 2 Charging Cable. Both ends of the cable are with type 2 AC connector.
◆ 1PH 32A 7.2KW Type 2 EV Home Charger. It provides a maximum power level of 7.2 kilowatts single phase 32 amps, with an operation voltage up to 250V.
◆ 3PH 16A 11KW Type 2 Charging Cable. It is performed using a dedicated charging station and/or home mounted wall box.
◆ 3PH 32A 22KW Type 2 AC Fast Charger. It allows the vehicle to be charged much faster than traditional slow charging methods.
◆ Type 1 to Type 2 EV Charging Cable. The cable has two connectors, one is type1 and the other is type2

4. DC Fast Charging Mode 4
Charging an electric vehicle gives you the freedom to go wherever you want with no worries about range anxiety. At home, work or on the go, if you want to make charging faster than a 240V wall outlet, mode 4 supercharger is the answer.Mode 4 DC fast charging is a more powerful version of EV charging that can deliver much higher rates of electricity to your vehicle in a short amount of time. This type of charging uses a direct current (DC) connection that delivers energy directly to the vehicle battery.
The charging capacity of Mode 4 charger can up to 350kw. This means that with an consumption of 17 kWh per 100km, you can achieve a recharge for a distance of 100km in just 45 minutes!
Charging Cable:
The charging cables have to be attached permanently to the Fast Charging Station and there is no flexibility in terms of charging positions. The other end of the cable is connected to the CCS2 EV inlet to directly charge the battery.
Mode 4 VS Mode 3:
The difference between mode 4 and mode 3 is that the charging gun of Mode 4 is connected to the AC grid or the DC power supply equipment at the DC grid end, that is, the DC charging pile, which is generally not for household use, but is specially installed at the fast charging station.
The charging current of mode 4 is larger, generally DC 80/125/200/250A, so the charging speed is also the fastest.
Message
If you are interested in our products, please fill in the message form below. Our sales representative will contact you within 24 hours.