Requirements for the Insulation Layer of EV High Voltage Cables
The selection of insulation materials is primarily based on heat resistance and mechanical strength. Compared to standard battery cables, softer materials can be reasonably selected to maintain the flexibility of specially designed stranded conductors.
The fundamental difference between high-voltage automotive cables and conventional cables is that the design needs to be rated for 600V, with voltage ratings exceeding 1000V for commercial vehicles and buses. In contrast, cables used in ICE vehicles are designed for a nominal voltage of 60V.
For all insulation materials, such high voltages are not a challenge. In industrial and civilian electrical systems, this still falls within the low-voltage range. However, for high-voltage cables in automobiles, the primary challenge lies in thermal and mechanical performance.
Since cables connect the battery, inverter, and electric motor, high-voltage cables are required to transmit high currents. Depending on the system's power requirements, the current can range from 250A to 450A. Such high currents are rarely found in conventional vehicles. The result of transmitting high currents is high power consumption and heating of the components. Therefore, high-voltage cables are designed to withstand higher temperatures. A growing trend indicates that temperature requirements are increasingly stringent. In contrast, cables in conventional vehicles are typically rated up to 105°C, which is sufficient unless the cable is located in high-temperature areas like the engine compartment. High-voltage cables for electric vehicles generally require higher temperature ratings, such as Class C (125°C) or Class D (150°C). In some cases, where routing conditions are adverse—such as near exhaust pipes, in front of the motor, or behind the battery—OEMs may specify even higher temperature resistance, such as Class E (175°C). The higher the temperature rating of the insulation material, the higher the rated current the cable can carry.
In contrast, cables in conventional vehicles are typically rated up to 105°C, which is sufficient unless the cable is located in high-temperature areas like the engine compartment. High-voltage cables for electric vehicles generally require higher temperature ratings, such as Class C (125°C) or Class D (150°C). In some cases, where routing conditions are adverse—such as near exhaust pipes, in front of the motor, or behind the battery—OEMs may specify even higher temperature resistance, such as Class E (175°C). The higher the temperature rating of the insulation material, the higher the rated current the cable can carry.
In the automotive industry, the expected service life of cables designed for specified temperature ratings is typically 3000 hours. This value is usually used in long-term aging tests according to recognized cable standards (such as GB/T 25085, GB/T 25087, QC/T 1037, and ISO 19642). Special requirements from customers in high-voltage applications may exceed 3000 hours, with the cumulative operating time reaching up to 12,000 hours. The heat resistance of the insulation material is proportional to its service life. The more heat-resistant the cable, the longer its service life.
The development of electric vehicles faces the challenge of integrating more electrical components into limited space. HV cables and connectors also require routing space, which often leads to tight bending radii. Due to the inherent design of conventional cables, high bending forces are difficult to overcome. To address this, high-flexibility design in high-voltage cables is crucial. Only with flexible designs can routing through the vehicle be achieved easily. If the motor is located near the vehicle's moving parts, causing continuous vibration of the connected high-voltage wiring harnesses, the cables need to be designed to withstand high-cycle bending to ensure excellent bend durability.
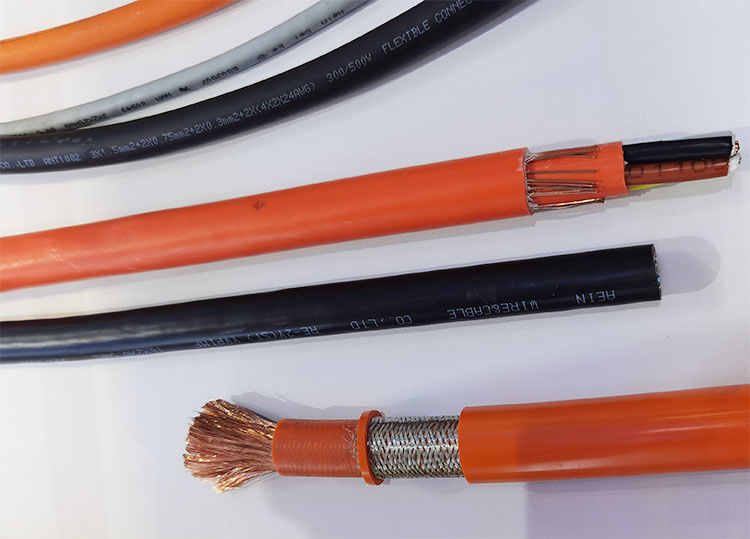
Given the complexity of the internal environment in electric vehicles, the primary considerations for selecting insulation materials are heat resistance and mechanical strength. This is one of the key differences between electric vehicles and traditional internal combustion vehicles. On one hand, the insulation layer must ensure safe usage, exhibiting excellent properties such as high and low temperature resistance, arc resistance, and resistance to electrical tracking. On the other hand, it is important to choose materials that are easy to process and widely used. Currently, commonly used insulation materials for high-voltage cables include PVC, cross-linked polyethylene (XLPE), silicone rubber, and thermoplastic elastomers (TPE). The key properties of these materials are summarized in Table 1.
◆ PVC contains lead, which is prohibited by the RoHS Directive along with other harmful substances such as mercury, cadmium, hexavalent chromium, polybrominated biphenyl ethers (PBDEs), and polybrominated biphenyls (PBBs). As a result, PVC has been gradually replaced by environmentally friendly materials such as XLPE, silicone rubber, and TPE in recent years.
◆ Among these materials, cross-linked polyethylene (XLPE) has the best tensile strength, gasoline resistance, and fire retardancy. XLPE can withstand temperatures as high as Class D (125°C), offering excellent mechanical strength and resistance to chemical effects from liquids. It can also be designed with more compact outer diameters. Overall, XLPE is widely used, although the parts in direct contact with the motor have a shorter lifespan.
◆ Silicone rubber (SIR) offers superior temperature resistance, softness, and aging resistance. Unlike D-class cross-linked polyethylene, which typically cannot achieve halogen-free status, silicone rubber is halogen-free, making it ideal for high-temperature, E-class high-voltage cable applications. Its excellent heat resistance, flexibility, and sealing properties, combined with minimal deformation under high temperature and pressure, make it particularly suitable for use in high-temperature environments or tight spaces with small bending radii.

◆ Thermoplastic elastomers (TPE) are primarily used for large gauge cables and communication wires.
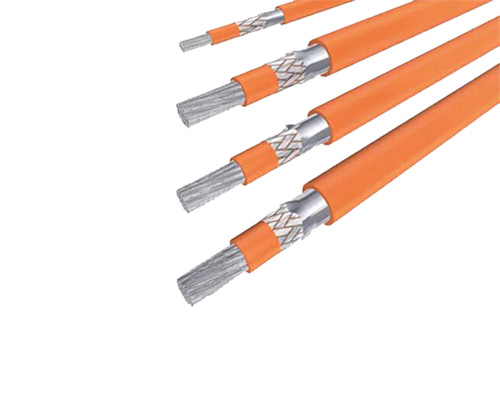
Warning signs and special markings, such as "Caution! High Voltage 600V" or the high-voltage lightning symbol, can also be printed on the cables. According to QC/T 414, orange is the designated primary color for high-voltage cables with a rated voltage > 30V AC / > 60V DC. To differentiate different circuits of high-voltage electrical systems, longitudinal stripes in auxiliary colors may be used as secondary colors. The recommended secondary colors are shown in Table 2. For armored cables, the secondary color may only be added to the insulation of the conductors and may serve as the primary color. For single-core cables, if the outer sheath is clearly marked, the insulation of the core wire can remain in its natural color (uncolored).
The fundamental difference between high-voltage automotive cables and conventional cables is that the design needs to be rated for 600V, with voltage ratings exceeding 1000V for commercial vehicles and buses. In contrast, cables used in ICE vehicles are designed for a nominal voltage of 60V.
For all insulation materials, such high voltages are not a challenge. In industrial and civilian electrical systems, this still falls within the low-voltage range. However, for high-voltage cables in automobiles, the primary challenge lies in thermal and mechanical performance.
Since cables connect the battery, inverter, and electric motor, high-voltage cables are required to transmit high currents. Depending on the system's power requirements, the current can range from 250A to 450A. Such high currents are rarely found in conventional vehicles. The result of transmitting high currents is high power consumption and heating of the components. Therefore, high-voltage cables are designed to withstand higher temperatures. A growing trend indicates that temperature requirements are increasingly stringent.

In the automotive industry, the expected service life of cables designed for specified temperature ratings is typically 3000 hours. This value is usually used in long-term aging tests according to recognized cable standards (such as GB/T 25085, GB/T 25087, QC/T 1037, and ISO 19642). Special requirements from customers in high-voltage applications may exceed 3000 hours, with the cumulative operating time reaching up to 12,000 hours. The heat resistance of the insulation material is proportional to its service life. The more heat-resistant the cable, the longer its service life.
The development of electric vehicles faces the challenge of integrating more electrical components into limited space. HV cables and connectors also require routing space, which often leads to tight bending radii. Due to the inherent design of conventional cables, high bending forces are difficult to overcome. To address this, high-flexibility design in high-voltage cables is crucial. Only with flexible designs can routing through the vehicle be achieved easily. If the motor is located near the vehicle's moving parts, causing continuous vibration of the connected high-voltage wiring harnesses, the cables need to be designed to withstand high-cycle bending to ensure excellent bend durability.

Insulation Materials for Cables
To prevent electric shock and short circuits, any cable used in electric vehicles should be insulated, and this is also true for high-voltage cable materials. The insulation layer in electric vehicles needs to tightly cover the conductor, not easily peel off, and must pass the 50Hz AC voltage-withstand test. If the cable does not break down during the test, it is considered qualified.Given the complexity of the internal environment in electric vehicles, the primary considerations for selecting insulation materials are heat resistance and mechanical strength. This is one of the key differences between electric vehicles and traditional internal combustion vehicles. On one hand, the insulation layer must ensure safe usage, exhibiting excellent properties such as high and low temperature resistance, arc resistance, and resistance to electrical tracking. On the other hand, it is important to choose materials that are easy to process and widely used. Currently, commonly used insulation materials for high-voltage cables include PVC, cross-linked polyethylene (XLPE), silicone rubber, and thermoplastic elastomers (TPE). The key properties of these materials are summarized in Table 1.
| Material | Density (g/cm³) | Heat Resistance (°C) | Flammability Grade | Advantages & Applications |
| PVC | 1.3 | 80 | UL 94 V-0 | Cost-effective and easy to process, but contains harmful substances, does not meet low smoke and halogen-free requirements, and is rarely used currently. |
| XLPE | 1.2 | 150 | - | High temperature resistance, non-flame retardant, stronger than the other three materials, suitable for high-strength applications. |
| TPE | 0.9 | 100 | - | Moderately priced, easy to process, low density, but has lower temperature resistance and is non-flame retardant, suitable for applications with moderate strength and temperature requirements. |
| SIR | 1.2 | 200 | UL 94 V-0 | Relatively expensive, resistant to both high and low temperatures, flexible, flame retardant, and complies with RoHS standards, suitable for high-temperature applications. |
Table 1: Comparison of Common Insulating Materials' Performance
◆ PVC contains lead, which is prohibited by the RoHS Directive along with other harmful substances such as mercury, cadmium, hexavalent chromium, polybrominated biphenyl ethers (PBDEs), and polybrominated biphenyls (PBBs). As a result, PVC has been gradually replaced by environmentally friendly materials such as XLPE, silicone rubber, and TPE in recent years.
◆ Among these materials, cross-linked polyethylene (XLPE) has the best tensile strength, gasoline resistance, and fire retardancy. XLPE can withstand temperatures as high as Class D (125°C), offering excellent mechanical strength and resistance to chemical effects from liquids. It can also be designed with more compact outer diameters. Overall, XLPE is widely used, although the parts in direct contact with the motor have a shorter lifespan.

Safety and Color Coding
Due to the increased application risks brought by high voltages, high-voltage cables must be visually distinguishable from regular automotive cables according to standards. The outer surface of high-voltage cables must be bright orange.Warning signs and special markings, such as "Caution! High Voltage 600V" or the high-voltage lightning symbol, can also be printed on the cables. According to QC/T 414, orange is the designated primary color for high-voltage cables with a rated voltage > 30V AC / > 60V DC. To differentiate different circuits of high-voltage electrical systems, longitudinal stripes in auxiliary colors may be used as secondary colors. The recommended secondary colors are shown in Table 2. For armored cables, the secondary color may only be added to the insulation of the conductors and may serve as the primary color. For single-core cables, if the outer sheath is clearly marked, the insulation of the core wire can remain in its natural color (uncolored).
| Color | Primary Color | ORANGE (OG) | ||||
| Secondary Color | RED (RD) | BROWN (BN) | BLUE (BU) | GREEN (GN) | Violet Tint (VT) | |
| Application | DC+ | DC- | AC wire 1 | AC wire 2 | AC wire 3 | |
Table 2: Recommended Color Combinations for High-Voltage Cables
Message
If you are interested in our products, please fill in the message form below. Our sales representative will contact you within 24 hours.