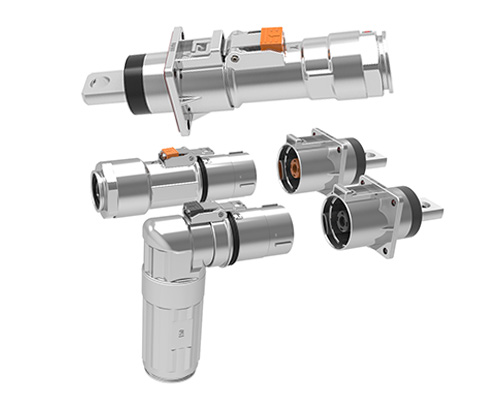
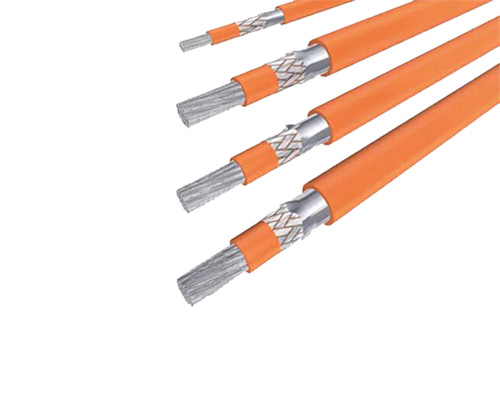
Classification and Construction of Electric Vehicle HV Cables
Electric vehicle high voltage cables are classified into:
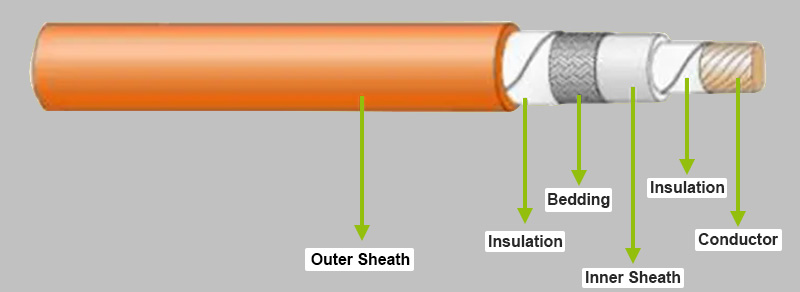
Cables with a conductive core and insulation sheath are called single-core cables. The insulated wires are surrounded by an insulating material that provides mechanical protection for the wires, as well as electrical insulation between the wires and other objects in the system.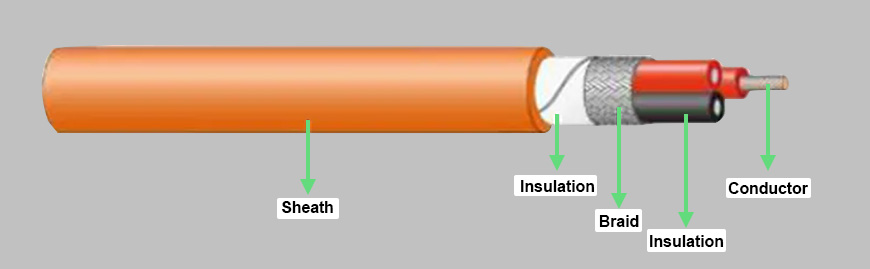 The multi-core cable is composed of multiple conductors and insulators, which are commonly grouped together in bundles. In essence, the electrical performance and size of each single-core wire is no different from that of a single-core cable. If there are wires for signal transmission in a multi-core cable, separate shielding measures are required to ensure that the signal is not lost.
The multi-core cable is composed of multiple conductors and insulators, which are commonly grouped together in bundles. In essence, the electrical performance and size of each single-core wire is no different from that of a single-core cable. If there are wires for signal transmission in a multi-core cable, separate shielding measures are required to ensure that the signal is not lost.
Shielded cables have an additional layer of insulation that protects the cable from electromagnetic interference (EMI) and radio frequency interference (RFI). The main purpose of shielding is to reduce interference from other devices in the proximity of the cable, and to prevent interference between the conductors inside the cable, which makes it possible for electric vehicles to operate more efficiently and safely. The shield of an electric vehicle high voltage cable can be made from different materials such as tinned copper wire braiding and aluminum foil.
The shielding design of the high-voltage wire harness includes the shielding of the high-voltage cable itself, the shielding of the joint between the high-voltage cable and the high-voltage connector, and the shielding of the HV connector.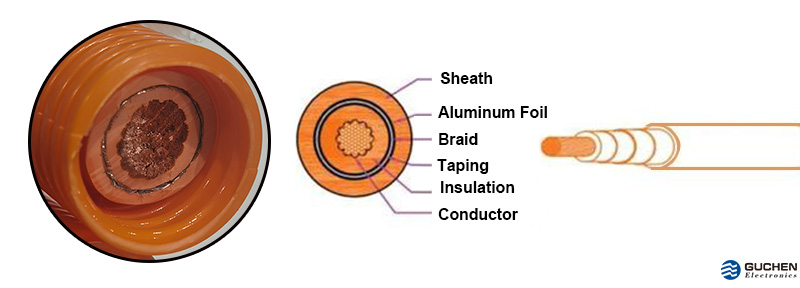 Unshielded cables do not have any additional insulation, so they are more susceptible to EMI.
Unshielded cables do not have any additional insulation, so they are more susceptible to EMI.
HV cable can be divided into copper core and aluminum core according to the material used for the conductor.
Copper is generally considered superior to aluminum for high voltage applications.
◆ It offers high mechanical strength (high ductility and malleability), which means that it can be easily bent into any shape without breaking. This is important for EV cables because they need to be able to flex around corners and curves in the vehicles. The malleability of the cable also makes it easy to work with, as it can be shaped into different configurations without being damaged.
◆ It has excellent electrical and thermal conductivity, which is why it is used for so many applications in electronics.
◆ It has a lower resistance than aluminum, allowing for higher current transfer.
◆ The other main advantage of this type of cable is that it has good tensile strength, which means it can withstand pulling forces without breaking or snapping. This is particularly useful when installing the cables in tension areas.
Therefore, copper cable is the most common material used in electric vehicle high voltage interconnection solutions.
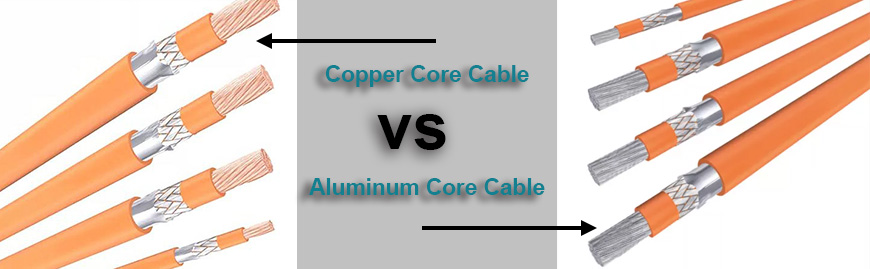
Aluminum's biggest advantage over copper is its cost - it's cheaper to manufacture an aluminum core cable than it is to manufacture a copper core one.
1. Single-core and Multi-core Cables
Cables with a conductive core and insulation sheath are called single-core cables. The insulated wires are surrounded by an insulating material that provides mechanical protection for the wires, as well as electrical insulation between the wires and other objects in the system.


2. Shielded and Unshielded High Voltage Cable
Shielded cables have an additional layer of insulation that protects the cable from electromagnetic interference (EMI) and radio frequency interference (RFI). The main purpose of shielding is to reduce interference from other devices in the proximity of the cable, and to prevent interference between the conductors inside the cable, which makes it possible for electric vehicles to operate more efficiently and safely. The shield of an electric vehicle high voltage cable can be made from different materials such as tinned copper wire braiding and aluminum foil.
The shielding design of the high-voltage wire harness includes the shielding of the high-voltage cable itself, the shielding of the joint between the high-voltage cable and the high-voltage connector, and the shielding of the HV connector.

3. Copper Core and Aluminum Core HV Cable
HV cable can be divided into copper core and aluminum core according to the material used for the conductor.
Copper is generally considered superior to aluminum for high voltage applications.
◆ It offers high mechanical strength (high ductility and malleability), which means that it can be easily bent into any shape without breaking. This is important for EV cables because they need to be able to flex around corners and curves in the vehicles. The malleability of the cable also makes it easy to work with, as it can be shaped into different configurations without being damaged.
◆ It has excellent electrical and thermal conductivity, which is why it is used for so many applications in electronics.
◆ It has a lower resistance than aluminum, allowing for higher current transfer.
◆ The other main advantage of this type of cable is that it has good tensile strength, which means it can withstand pulling forces without breaking or snapping. This is particularly useful when installing the cables in tension areas.
Therefore, copper cable is the most common material used in electric vehicle high voltage interconnection solutions.

Message
If you are interested in our products, please fill in the message form below. Our sales representative will contact you within 24 hours.