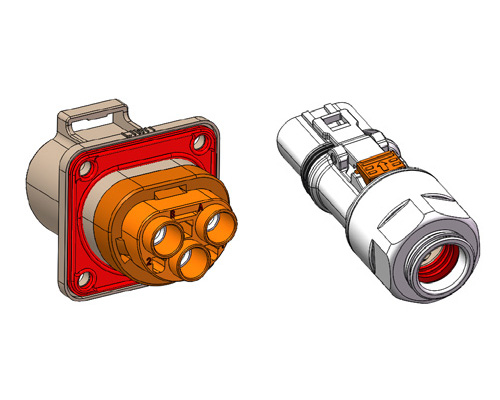
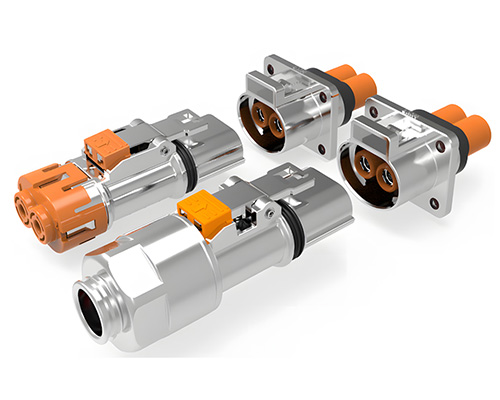
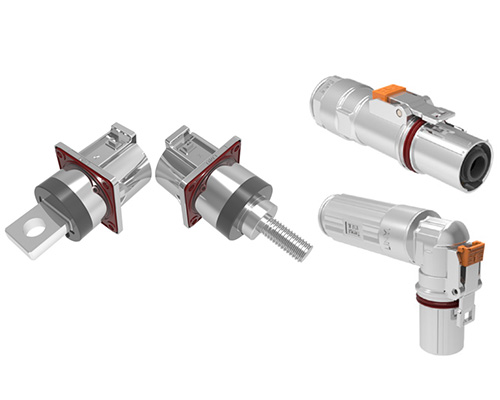
As the core component of the energy storage system, the lithium battery is the primary factor affecting energy storage safety. Fire is the most common cause of damage to
lithium-ion battery energy storage systems. Under various complex working conditions, batteries have potential for sudden combustion and explosion phenomena caused by internal failures or external ignition sources such as overcharge, short circuit, lightning strikes, electrical arcs, extrusion, vibration, collision, etc.. When a fire occurs, the battery pack temperature will rise rapidly and the pressure inside the battery pack becomes higher than atmospheric pressure outside. If there are any leaks in the battery pack during this process, they will become much worse when exposed to high temperatures.
In BESS, a single battery releases a large amount of heat when thermal runaway occurs, and the heat is transferred to adjacent batteries through convection, radiation, conduction, etc. When the temperature of adjacent battery cells reaches the thermal runaway trigger temperature, thermal runaway propagation is induced. This phenomenon can result in significant damage to surrounding equipment and facilities.